Mumps is a viral disease that is commonly referred to as Epidemic Parotitis. It is a highly contagious disease that results in the inflammation of either one or both of the parotid glands. Mumps can easily be prevented by taking the MMR vaccination during childhood.
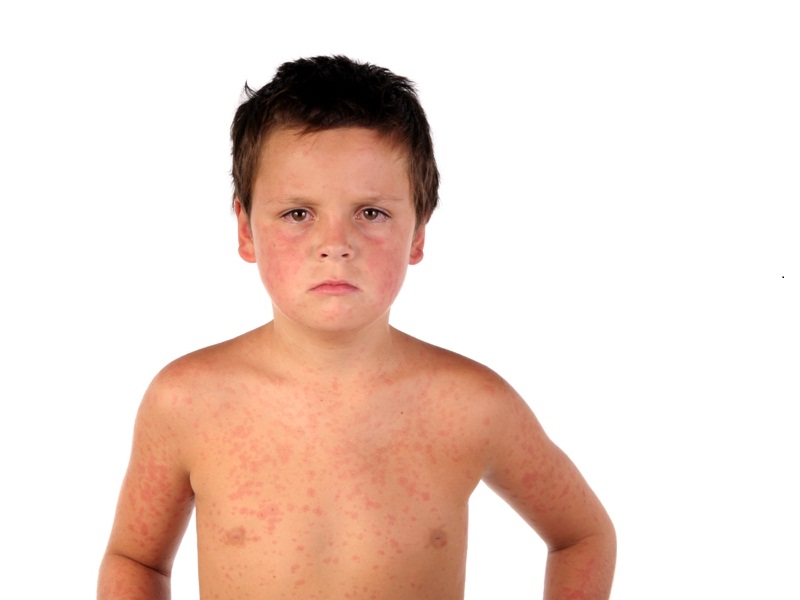
Mumps is a very contagious viral infection that has been noted to affect small children. There have been over 1200 cases per year of mumps where the swelling of the two salivary glands on both sides of the face is involved giving the person a more hamster-like face. The mumps virus is a contagious virus and can be transferred by touch or the use of common tools. Once a child usually has mumps, they are immune to almost all other diseases their entire life. This may be the only upside of having this disease.
Mumps can be extremely painful as the glands swell more and more due to infection. Warm water towels may help reduce the swelling to a certain extent. There is a great deal of tension to be taken over how long your child may suffer from this.
Normally mumps last for a little over a month giving the person an ample amount of discomfort; normally doctor prescribed medication may help in reducing pain. Antibiotics help to fight infection and in the long run, reduce the swelling but you cannot give a child too many antibiotics as it will no doubt mess with their system.
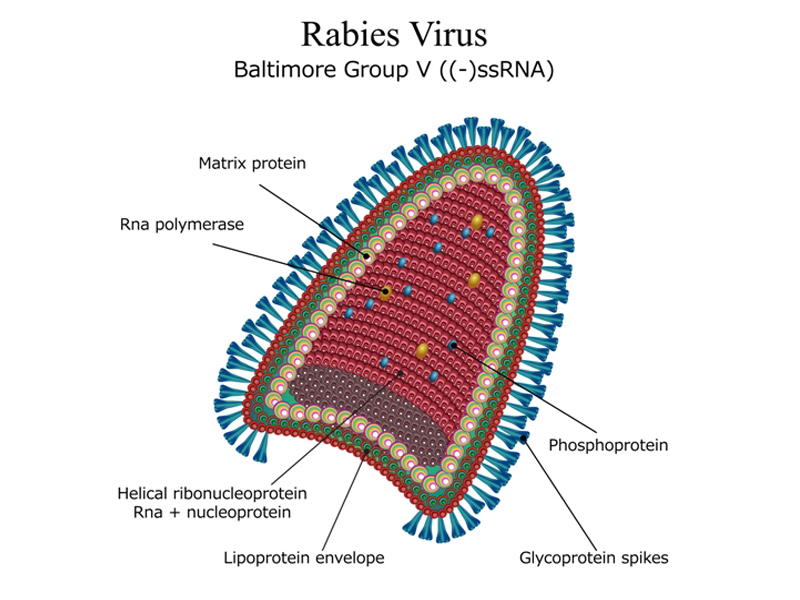
Mumps is mainly caused due to Rubulavirus infection. The infection then spreads from one person to another through the medium of infected saliva. When you contract mumps infection, the virus reaches your salivary glands from the respiratory tract. There is further reproduces and causes swelling in the glands.
Mumps Symptoms and Causes:
Here in this article will explain about what are the main reasons or causes and symptoms of mumps.
Causes Of Mumps:
There are a few reasons or causes of Mumps, some of which are mentioned in detail below:
1. Direct Contact:
Direct contact with another person who already has this infection may cause you to start having this infection yourself. Especially with children constant interaction may cause the transfer of mumps virus from one child to another. This is why it is necessary to give your child the vaccine responsible in the aide of fighting this virus. The vaccine helps to keep your body immune to mumps therefore ensuring that you and your child lead a healthy life free of infection and viruses.
2. Indirect Contact:
Indirect contact for example when a child uses the tap used by a mumps patient then it is possible residue of the virus on the tap may infect the child too. Indirect contact is one of the main ways you or any child can get mumps. Mumps generally occurs in children because their immune system is still developing therefore they do not have strong enough systems to fight off this virus effectively.
To aid in the battle against the spread of mumps, the MMR vaccine is commonly given at an early age to help the body become immune to the virus. Before the MMR vaccination was brought in, in England and Wales, there were 1,200 cases involving hospital admission per year.
3. Other Ways In Which The Mumps Virus Can Be Spread are:
Sneezing or coughing using the same cutlery/plates with someone infected sharing food and drink with someone infected kissing someone infected touching their nose or mouth and then passing it onto a surface someone else may touch. All these causes actually play an active part in a child’s infection. The virus moves up the respiratory tract into the salivary glands and reproduces causing the glands to swell greatly. This swelling can cause a great deal of discomfort in the face therefore the urgent need for doctors’ attention along with the MMR vaccine is required at the right time.
See More: Measles Symptoms
Symptoms Of Mumps:
There are very distinctive symptoms that help us determine whether our children have Mumps or not; some of these signs and symptoms are:
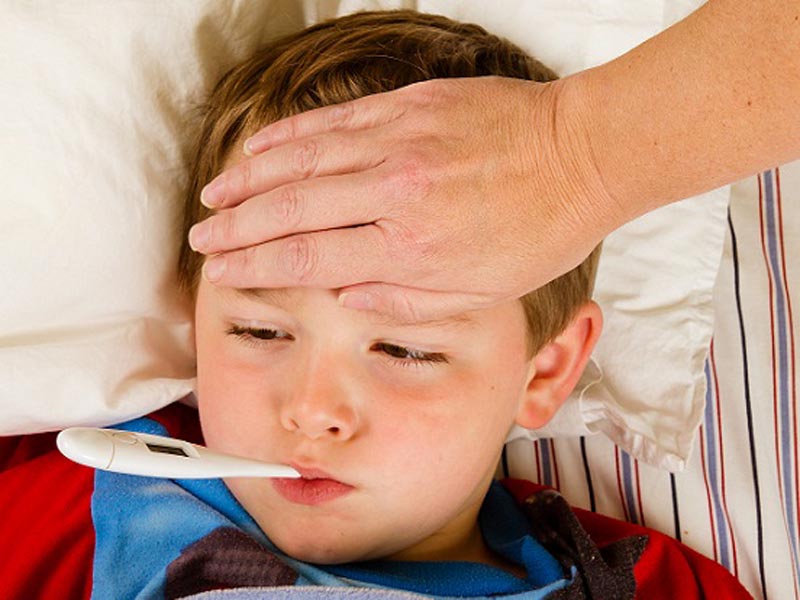
1. Pain In The Sides Of The Face:
It normally begins with pain in both sides of the face. This shows that the virus has entered your body and moved onto the glands on both sides of your face. If you do not go to a doctor at this point, there is no holding back the swelling that will start after a short period of time.
2. Swelling:
Once your cheeks start to swell, on both sides there is no going back at this point the virus has already started producing in the glands located on both sides of your face. The swelling will continue to increase as long as the virus keeps producing. You can help fight this virus by taking doctors-prescribed medication, and if you are lucky this virus will slowly dissipate over time.
3. Difficulty In Swallowing:
Sometimes mumps infection also causes difficulty in swallowing, also known as dysphagia. In such conditions, the person finds it difficult to eat or drink. In mild dysphagia, you might experience difficulty in eating for just a minute and taking a few sips of water will tend to make the condition better. However, in acute cases, it restricts the intake of food and the person is devoid of essential calories and nutrition required for normal functioning of the body.
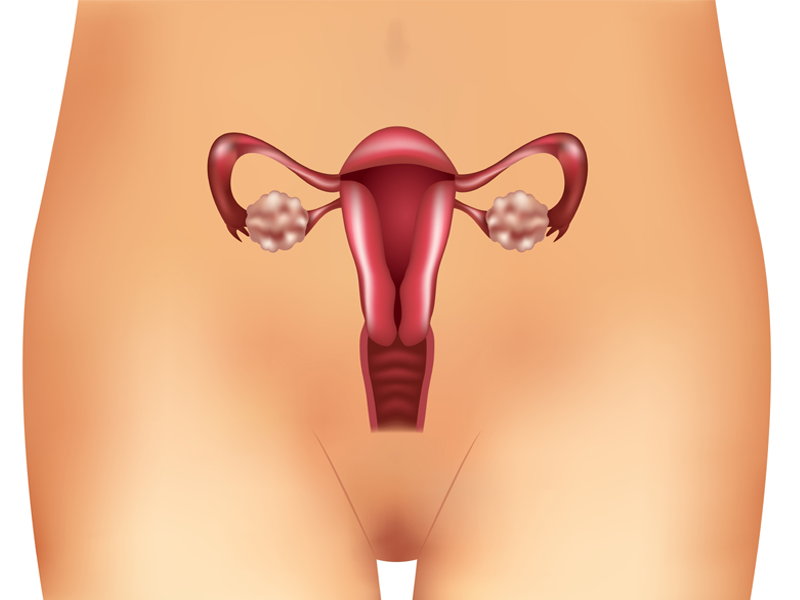
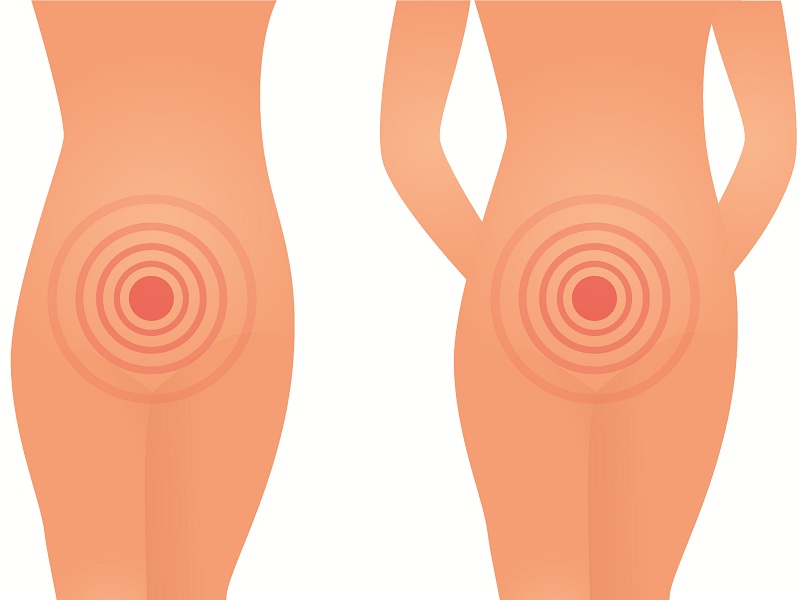
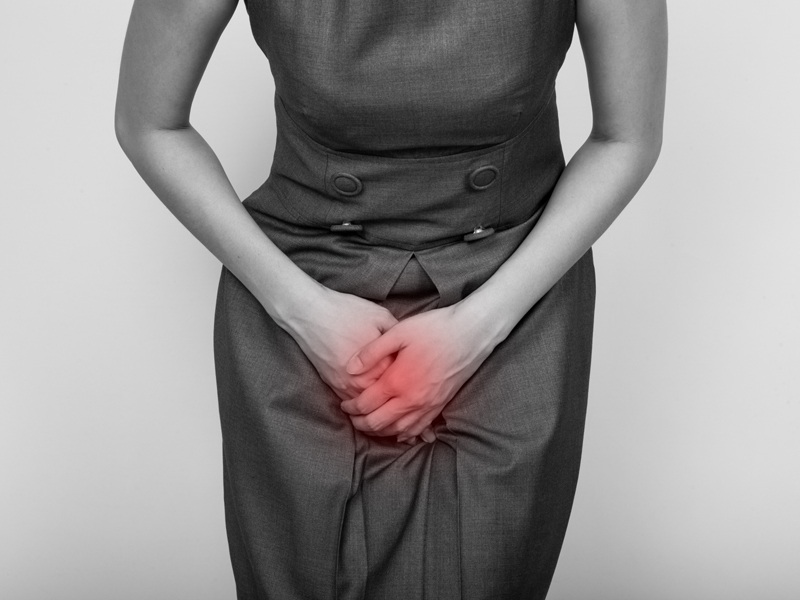
4. Orchitis:
Orchitis is a medical condition that refers to inflammation or swelling in either or both testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. It is a very uncommon symptom of mumps that surfaces when the infection gets very severe. Orchitis causes swelling and tenderness in the testicles and the condition is very painful. In most of the cases of mumps infection, the inflammation is commonly seen only in one testicle and affects both only in rare cases.
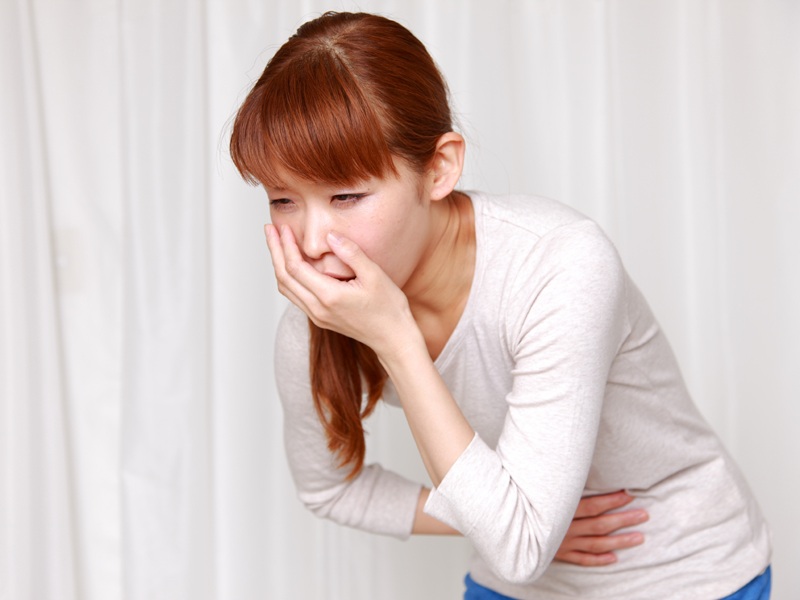
5. Nausea:
Nausea is another symptom of mumps. Mumps causes an imbalance in your body which in turn causes you to feel sick due to the swelling in your face. Nausea is caused because the virus in your glands is causing a dysfunction in your body making you feel sick and tired.
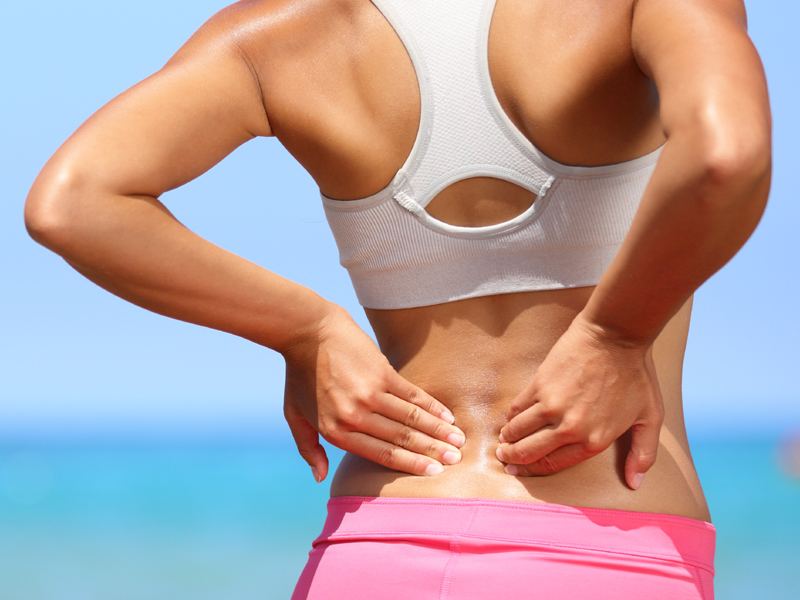
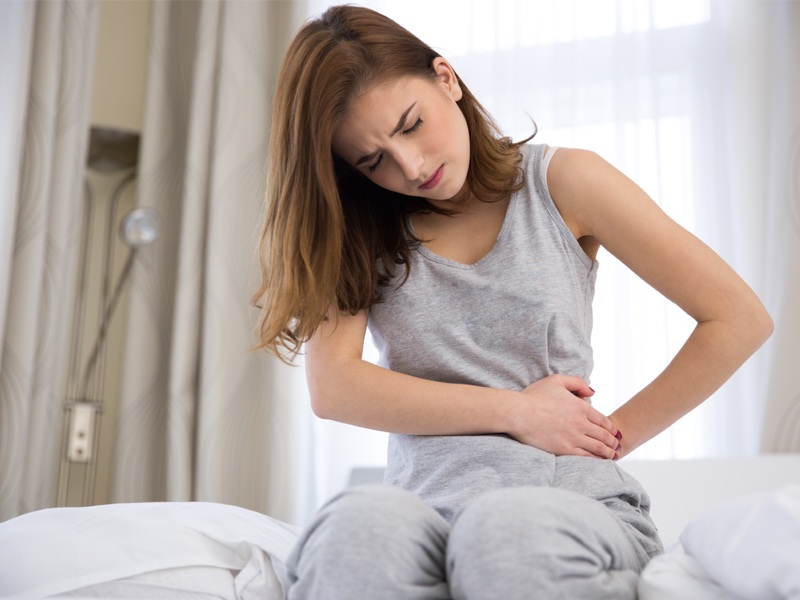
6. Abdominal Pain:
Mild abdominal pain is also known to be one of the common symptoms of mumps. During a mumps infection, you can experience pain in your stomach, and the lower or upper parts of your abdomen. The pain can vary from very mild to severe, depending on the stage of infection. When you begin to experience sharp abdominal pain, consult your physician immediately. Your GP might suggest a few tests and through physical examination ascertain the exact cause of the pain.
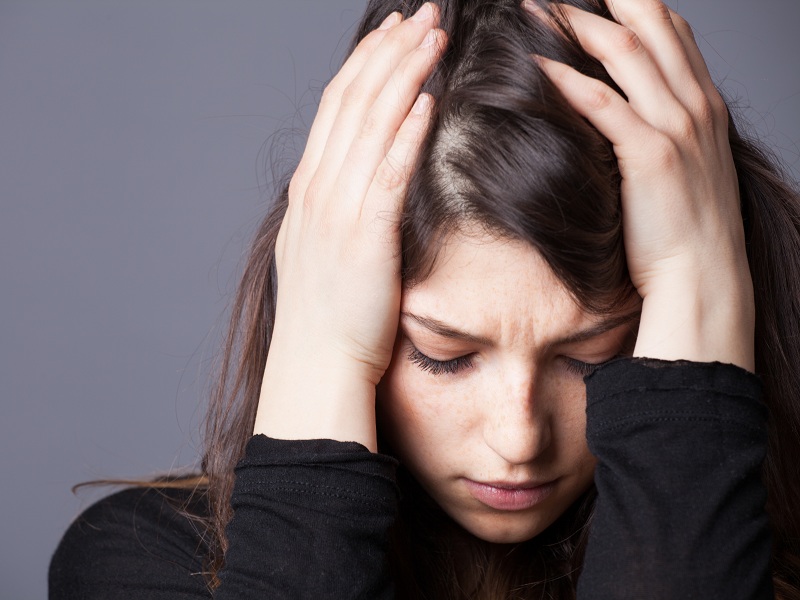
7. Headaches:
Primarily headaches are the first symptoms of mumps. Large build-up of mucus in the brain causes a strain which in turn causes headaches. Headaches can range from very mild and manageable to very bad and excruciating. Mild headaches are not that bad and you can determine that if you have mumps, then the headaches may be severe in nature as the face feels constantly swollen. Excruciating headaches which occur every day a very bad signs. Though mumps is not fatal, it can cause a large amount of discomfort.
8. Loss Of Appetite:
Loss of appetite is also seen to be one of the common mumps symptoms. Due to swelling in the salivary glands, the person with mumps infection finds it difficult to chew the food. Due to pain or discomfort, you might not feel like eating or drinking anything. This ultimately results in a loss of appetite
9. Lethargic:
Mumps causes extreme lethargy in the patient suffering from these problems. The irregular blood distribution in your body causes this lethargic feeling. Along with irregularity mumps also causes the virus to enter your bloodstream to also cause lethargic behavior. Lethargy may cause you to feel tired and weak even when resting. Along with lethargy, you may develop a fever therefore these are the telltale signs of mumps.
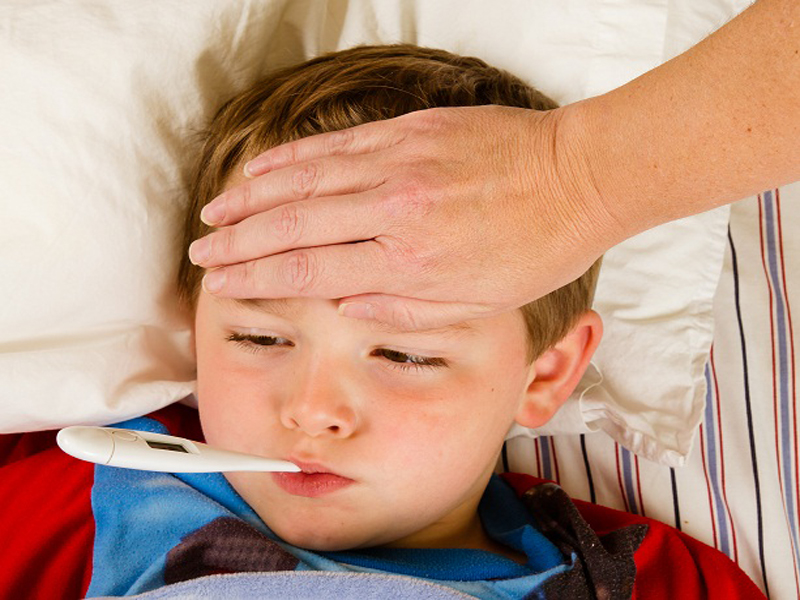
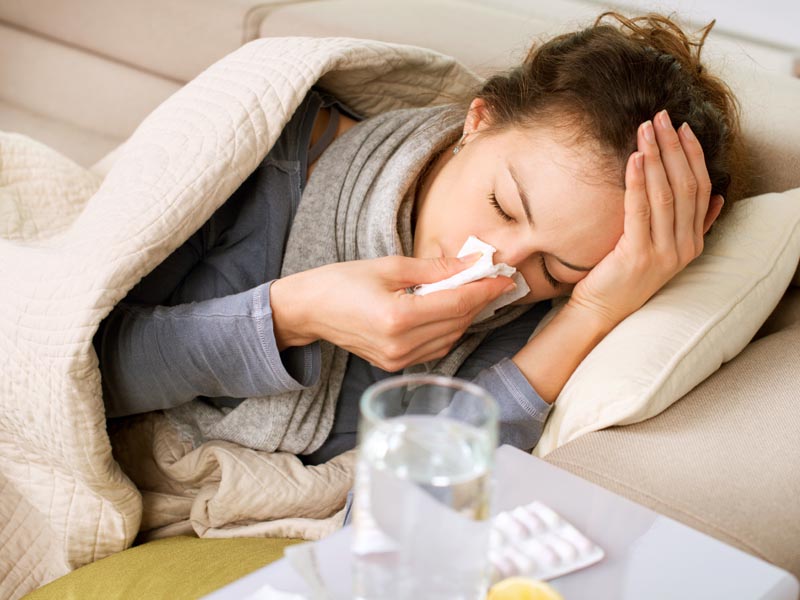
10. Fever:
Be careful with what you or your child touches throughout the day and who they come in contact with; a strong healthy household can save your child from a ton of discomfort that could otherwise make their lives a little harder. Fever during mumps infection is only moderately high and lasts for only 3-4 days.
Most of these symptoms of mumps do not appear immediately and develop within 14-25 days of the infection. This period is called as incubation period and on average is about 17 days. However, in nearly 20% of mumps infection cases, the virus does not exhibit any noticeable symptoms. When you suspect of mumps infection, do not wait to discuss the condition with your doctor. Most of the symptoms of mumps are often confused with that of tonsillitis or glandular fever. Your GP may examine and then confirm (or rule out) mumps infection.
Like all other viral diseases, our body’s immune system fights foreign infections. In most cases, no treatment is required and the infection consequently subsides in a few days. Eating soft foods and shunning acidic and citric foods helps to ease the symptoms.