Are you noticing sudden changes in your body – both mental and physical during your pregnancy? Are you moody often? Do you have sudden weight gain or loss? Then, it may be the Thyroid! Thyroid during pregnancy is among the most common conditions for most women. The two thyroid diseases – hypo and Hyperthyroidism- are widespread and easy to treat and regulate. If you are suffering from thyroid hormone during pregnancy, want to know how it works, how to take care, dialogize, prevent and treat the hormone, and keep reading!
What Is Thyroid, And How Does The Thyroid Hormone Affect Pregnancy?
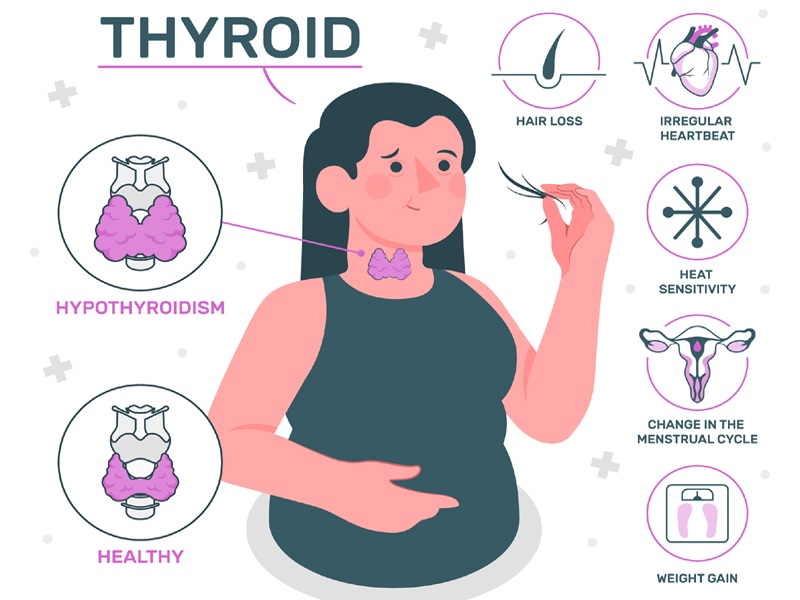
Popularly known as thyroid hormone disorder, the diseases include Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism. They are quite common and regularly found in pregnant women. The Thyroid is an organ that regulates one’s metabolism, nervous system, and heart and is located in the neck.
While studies say that around five or more per cent of women commonly acquire thyroid disease during pregnancy (1), the right and controlled or balanced hormone is required for a healthy mother and fetus. Given that the baby relies on the perfect hormones for brain and nervous development, the fetus’s thyroid gland may be affected by the mother’s abnormal thyroid levels.
But why do pregnant mothers often see a rise in their thyroid levels? The two pregnancy hormones, estrogen and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), often contribute to abnormal levels. One should regularly conduct tests to determine if the condition exists for the mother-to-be. Left untreated, several difficulties may occur, such as placental abruption, miscarriage, growth restriction, and more (2).
Let us know all about the types of Thyroid in a pregnant woman that may occur and how to manage them.
See More: Gestational Diabetes Symptoms and Treatment
What Are The Main Types Of Thyroid Conditions In Pregnancy?
As mentioned, there are two types of main pregnancy time thyroid conditions. Here are two types of thyroid disorders commonly known (3).
Hypothyroidism:
In Hypothyroidism, also known as underactive Thyroid, the adult’s thyroid hormone is deficient. It is also known as Hashimoto’s disease or autoimmune disorder, which may cause thyroid gland inflammation. Here, the thyroid gland is not producing enough hormones required. It is often affected mostly by women who are already diagnosed with the disease in the past or even by those who have a family history of experiencing the condition.
Hyperthyroidism:
Hyperthyroidism is having an overactive thyroid gland. Here, the gland produces more Thyroid than required for the body and metabolism. Henceforth, this condition speeds up the metabolism of the body. It is also called Grave’s disease in expecting mothers-to-be or during pregnancy.
Let us know all about Thyroid for pregnant ladies, how to diagnose them, causes, and treatment.
Hypothyroidism In Pregnancy:
As we have seen, the case of Hypothyroidism in the pregnant mother is where the body does not produce enough or required hormones. This may cause sluggishness, slow mental and physical fitness functioning, and overall health. This may have several causes and effects, and the symptoms quite range differently for several women according to their body changes. The reasons, symptoms, and diagnosis treatment for Hypothyroidism in pregnancy include (4),
Causes:
Hashimoto’s disease is the most common and frequent reason for Thyroid during pregnancy(Hypothyroidism). This autoimmune disorder causes the immune system to attack and produce antibodies against the thyroid gland.
Another common cause of Hypothyroidism is also due to heavy medication or treatment for the overactive thyroid gland. Those with a family history or previous thyroid gland disorder can often cause the condition again.
Symptoms:
Although the symptoms may not be the same for all pregnant ladies, the most common ones for thyroid disorder during pregnancy include,
- Tiredness and lack of body energy
- Closing eyelids
- Weight gain or heavyweight changes
- Constipation
- Swollen face
- Joint pain
- Dry or coarse skin and hair
- Muscle cramps
- Slow pulse concerns
- Pains near hands
- Anxiety and confusion
The symptoms listed above may not show immediately and are hard to notice sometimes. Most ladies and pregnant mothers miss out on the early stages of thyroid disease, given no record or symptoms spotted.
Effect Of Hypothyroidism On Pregnant Lady And Baby:
Hypothyroidism may have several adverse effects on the pregnant mother. If not diagnosed or treated on time, these thyroid and pregnancy complications include miscarriage, muscle pain and extreme weakness, congestive heart failure, placental abnormalities, pre-eclampsia, and postpartum haemorrhage or bleeding. These thyroid problems in pregnancy may increase if there is a severe hypothyroidism issue.
There may also be critical effects on the fetus and baby’s development. The baby’s brain and physical development depend on the perfect functioning of the thyroid gland. If not recognized, the baby may have neurological, cognitive, and other developmental abnormalities (5).
How To Diagnose:
Generally, the health care provider or endocrinologist will perform a comprehensive physical examination and thyroid test profile to detect and diagnose the condition of Hypothyroidism. Blood samples are collected to test the thyroid gland in three forms, T3, T4, and TSH, to understand if the gland works correctly. This thyroid test helps to understand thyroid levels during pregnancy. Further, as required, previous medical histories and family medical records may be sought to understand thyroid functioning in the body.
How To Treat Hyperthyroidism During Pregnancy:
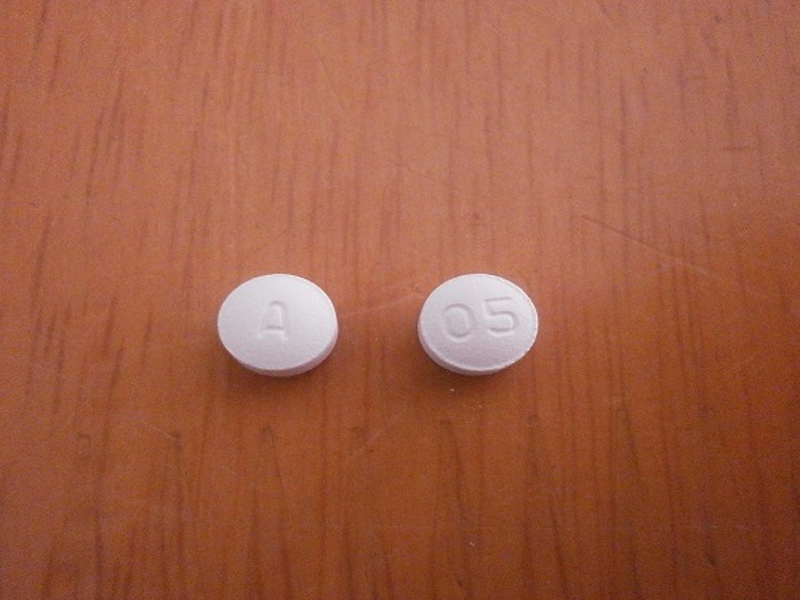
Depending on the level of TSH, the medical practitioner will treat the Hypothyroidism in pregnant ladies by replacing the thyroid hormone. Dosages of Levothyroxine/Thyroxine are given as required to reactivate the underactive thyroid concern in pregnancy. Higher dosages may be prescribed initially by the doctor to increase the thyroid hormone levels and balance out the glands under activeness. If pregnant women already have the issue before conceiving, the dosages may be increased as required by the doctor (6).
Further, regular testing and diagnosis should continue to regulate and monitor the level of the Thyroid. For pregnant ladies and moms-to-be, routine thyroid examination is conducted at specified intervals to track the gland. Additional medications and vitamins will be given as the physical requirement of the mother.
See More: Hypothyroidism in Pregnancy
Hyperthyroidism And Pregnancy:
On the other hand, Hyperthyroidism is an overactive thyroid gland that the body needs or requires. This leads to an increase in the metabolism of the body rate. Here are the causes, symptoms, and treatment related to Hyperthyroidism (7) (8).
Causes:
Graves’ disease is the most common reason for Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy. This autoimmune disorder may lead to too many thyroid hormone-making antibodies than required. This, in turn, leads to an increase in the thyroid gland or swollen Thyroid. Another uncommon cause may be high pregnancy hormone levels, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Symptoms:
The most common Hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid symptoms during pregnancy include the following.
- Heavyweight loss or drastic weight loss
- Heavy eating and metabolism rate
- Trouble in sleeping patterns
- Rapid heartbeat
- Feeling irritated
- Anxiety
- Sweating
- Shaking or shivering hands and fingers
- Weakness in muscle areas
- Redness or irritation near the eyes
- Diarrhea
- Irritated bowel and abnormal bowel moments
While hyperthyroidism symptoms may not be observed or spotted immediately, they may begin to appear over time.
Hyperthyroidism Effect On Pregnant Lady And Baby:
There may be severe complications and concerns if the hyperthyroidism condition is left untreated for pregnant mothers. This Thyroid can affect pregnancy adversely. Ill-treatment or no treatment may lead to pre-eclampsia and early labour. The other problems include fetal loss, the baby’s low birth weight, and the fetus’s abnormal development (9).
Timely intervention and treatment are required to avoid grave complications and worsening of pregnancy in the third trimester.
The uncontrolled Hyperthyroidism for the mother may lead to several concerns for the baby. Premature babies, stillbirths, faster heartbeat rates, malformations, and congenital disabilities are commonly observed due to this condition. These too-high hormone levels abrupt and work against the baby’s thyroid gland. There are also cases of neonatal Hyperthyroidism due to Grave’s disease of the mother.
How To Diagnose Hyperthyroidism:
The usual thyroid tests are taken through blood samples to observe the T3, T4, and TSH levels to understand thyroid problems while pregnant. Based on the reports, physical examinations, and other symptoms, the health care provider or doctor will give apt medicines and treatment required for a healthy pregnant lady and baby.
How To Treat Hyperthyroidism During Pregnancy:
Depending on the severity and concerns of the condition, the treatment options for Hyperthyroidism may differ. The mild levels can be regulated by medicines only. Antithyroid medications and pills are prescribed. These help block the Thyroid from producing new hormones in the body.
If this method is impractical, surgical procedures can be used in the second trimester to remove the excess thyroid gland. This extreme method may be taken to regulate the concern completely. Another common practice is Radioiodine to treat Hyperthyroidism in pregnant mothers. This destroys the thyroid gland and may sometimes also lead to hypothyroidism concerns.
Endocrinologists can use Beta-blockers to control the situation in case of heavily impaired fetal growth and severe complications.
Postpartum Thyroiditis:
Postpartum Thyroiditis, although rare among new mothers, is the condition of having an inflamed thyroid after having a baby. The heavy inflammation pushes the thyroid hormone to leak from the thyroid gland, raising hormone levels in the blood and resulting in Hyperthyroidism.
While Hyperthyroidism may lead to a couple of months, the underactive Thyroid later converted on (Hypothyroidism) may last till a year. Here are the possible causes, symptoms, and treatments for Postpartum Thyroiditis.
Causes:
Like Hashimoto’s disease or the autoimmune condition, Postpartum thyroiditis is only caused after the pregnant lady gives birth. The situation is rare to take place. However, it is treatable.
Symptoms:
Often, thyroiditis symptoms are mistaken for sickness or tiredness due to giving birth to one’s baby. Since the condition is caused after giving birth, symptoms include tiredness, moody feelings, and cramps. Hypothyroidism’s other symptoms may also be prevalent, such as trouble sleeping, dry skin, tingling in the hands or legs, coldness, etc. It is essential to consult and talk to the doctor immediately if you feel moodiness and tiredness to check and diagnose the condition.
Diagnosis:
Any of the symptoms mentioned above can be observed in the new mother; the doctor conducts blood tests and physical examinations to check and understand the thyroid hormone levels.
Treatment:
The treatment for thyroid disease during pregnancy and postpartum differs from person to person. Most times, this does not need any treatment and can be set right after a few months of giving birth. However, if the condition gets troublesome, the doctor can examine and prescribe medicines such as beta-blockers to reduce excessive heart rate control. Most antithyroid medications may not work in this situation unless the new mother already has Grave’s disease.
Gradually, if there are Hypothyroidism symptoms after a few months, the doctor may accordingly examine, diagnose, and prescribe the medicines to help bring the hormone to control.
Diet To Follow During Pregnancy For Thyroid Control:
For pregnant mothers, a specific regulatory diet must be followed to control and balance the thyroid hormones. It is essential to avoid and intake certain foods and diet accordingly for the best health of the mother and the unborn baby (10). The advised thyroid diet for pregnancy is,
- A healthy diet is crucial. It is good to have a satisfactory intake of fruits and vegetables, including whole grains.
- Healthy oils such as olive oil are recommended during the cooking process
- Proteins are good for health. Lean-source protein such as from fish is highly recommended
- High iodine content should always be avoided
- Avoid high amounts of soy and related proteins
- Cut down on bad carbs and fats. While nuts, seeds, legumes, cheese, milk, and other trans fats are good to go, it is advised to minimize soft drinks, alcohol, refined sugary drinks, sugar substances, chips, packaged foods, candy, and more junk foods.
- A high intake of dietary fibre is always a plus.
See More: Blood Pressure in Pregnant Women
Workouts And Lifestyle Activities Suggested For Controlling Thyroid During Pregnancy:
Regular exercise and an active life are recommended, along with medications to control the Thyroid during pregnancy. A daily routine can help better control the Thyroid and overall wellness, fitness, and smooth pregnancy. It boosts metabolism, improves sleep, and improves mood and energy too.
Low-impact exercises and workouts without any stress are recommended to pregnant mothers during pregnancy. Walking, yoga and swimming are most commonly advocated. However, it is recommended to always check your health condition and overall physical fitness with your health care provider before doing any exercise or fitness regime all by yourself.
Thyroid during pregnancy is the most commonly known condition for several mothers-to-be. We hope this well-researched and detailed guide on the condition helps better understand the symptoms and condition. Please check with your doctor for further details and personalized checks in case of thyroid treatment for pregnancy.
Disclaimer:
This guide on Thyroid hormones during pregnancy is only for informatory and knowledge purposes. Please check with your family health doctor or medical professional for further input and overall health profile. Do not take any medication, treatment, or steps alone without involving the health care provider.