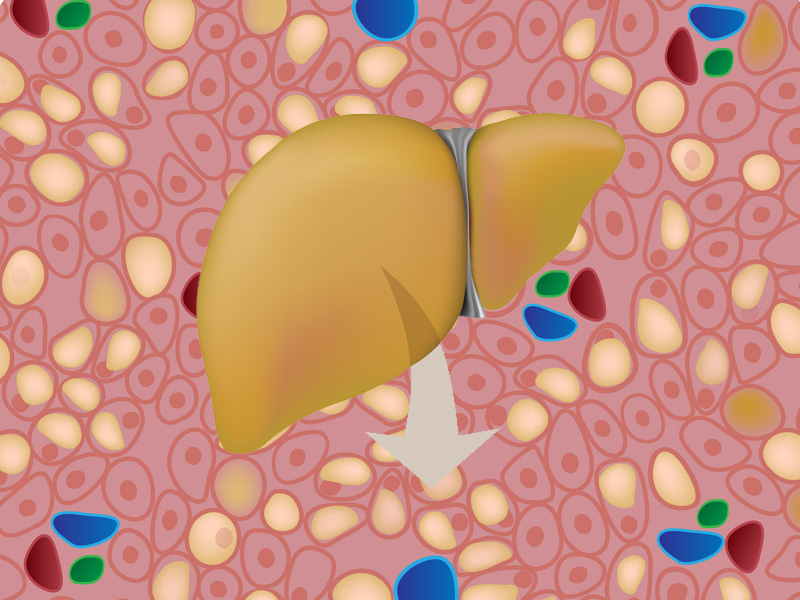
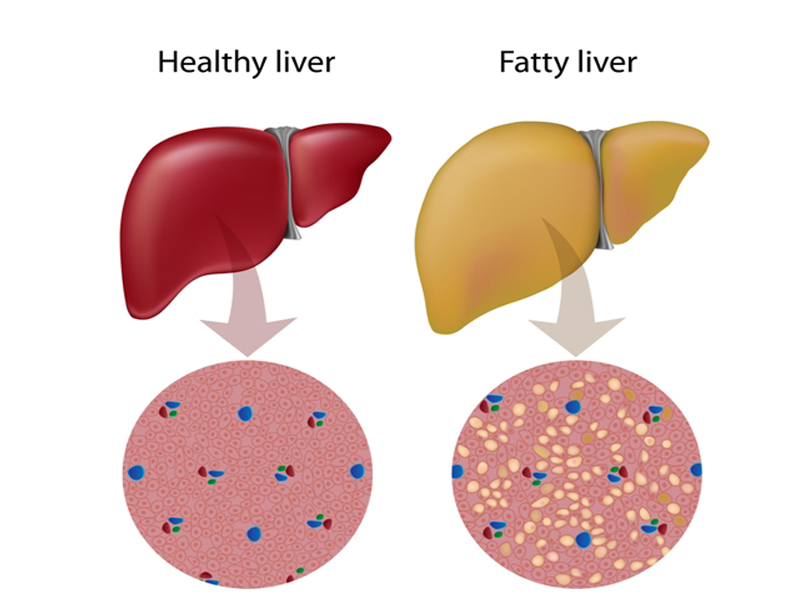
Fatty Liver Disease has become one of the most common health problems in the modern world. As the term suggests, it occurs when there are excess deposits on the liver, which prevent it from functioning normally. The result? You are likely to experience poor digestion, weakness, weight loss and, in extreme cases, death! Learning about Fatty Liver causes and symptoms can help you take the right action early and save your life!
But before that, you need to know that there are two types of Fatty Liver Disease – Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD).
In this article, we shall discuss the causes and symptoms of fatty liver of both these types, to gain a thorough understanding of the problem.
What Are The Causes of Fatty Tissues on Liver:
Fatty Liver Disease, also called Hepatic Steatosis, is caused when the liver of overburdened with excess fat. When the fatty liver occurs in a person who consumes a lot of alcohol, it is called Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) and a fatty liver formed in non-alcoholics is called Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).
Let us look into each of the causes of these two types of Fatty Liver disease in detail:
Alcoholic Fatty Liver-
As mentioned earlier, Alcoholic Fatty Liver is caused due to excess consumption of alcoholic drinks. Let us find out how alcohol affects the health of your liver and cause fatty liver disease:
1. Alcohol:
People who consume approximately 3 ounces or more of alcohol are at a higher risk of developing Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. This is because our liver can break down only a certain amount of alcohol at a time. When this level goes up, the liver undergoes tremendous pressure and releases toxic substances that lead to inflammation.
Increased levels of alcohol in the body can increase the severity of the disease and may ultimately lead to liver cirrhosis and failure.
Read: Risks And Side Effects of Alcohol During Pregnancy
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver:
This is a type of fatty liver disease that is not caused because of alcohol. Let us look into some of the common causes of NAFLD and their impact on your liver:
2. Obesity:
Obesity is one of the main causes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. It is a condition in which the body has excess fat deposits due to poor lifestyle or high-calorie diet. This can increase the fat content in the liver, leading to Simple Fatty Liver.
Also, studies show that abdominal obesity is closely linked to insulin resistance, in which the effects of insulin on the body are reduced. In this process, the liver may undergo cell damage and inflammation leading to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) (1).
3. Metabolic Syndrome:
Metabolic Syndrome is another major risk factor for fatty liver disease. It is a condition in which several abnormalities like obesity, hypertension etc. occur within the body. One way to identify this syndrome is a large waist circumference in the affected person. As mentioned earlier, abdominal obesity is linked to insulin resistance and higher BMI levels. Both of these factors increase the risk of liver damage.
4. Rapid Weight Loss:
Although weight loss is a recommended treatment for fatty liver, rapid reduction in weight can prove to be dangerous in this condition. Experts warn that losing weight too quickly can result in a fulminant hepatic failure, often leading to death. Weight loss has to be a gradual process, and a person must aim to shed no more than a few pounds per week using a combination of exercise and a low-calorie diet.
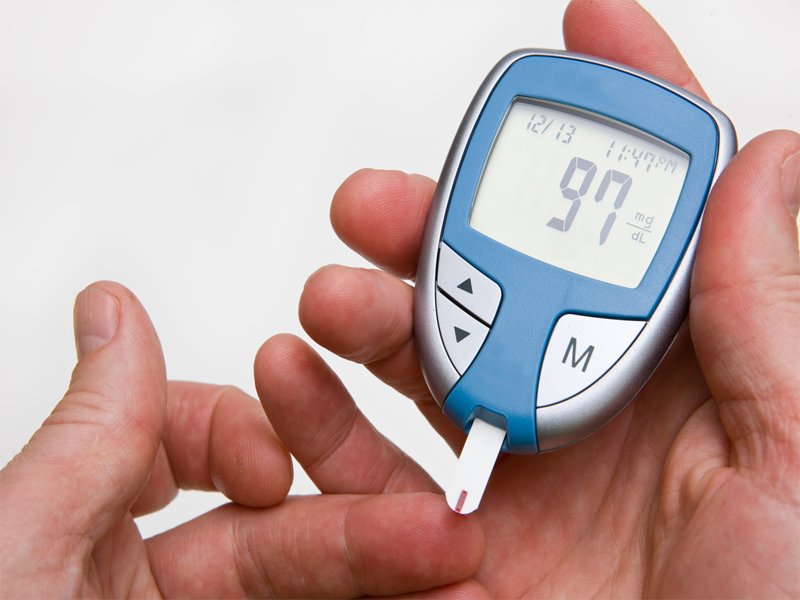
5. Pre-Diabetes or Type-2 Diabetes:
People having pre-diabetic conditions or Type-2 diabetes have a higher risk of getting NAFLD. The reason? Type 2 Diabetes often causes Obesity and Insulin resistance, which are the main causes of Fatty Liver Disease. Also, in patients suffering from Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus, there is a co-occurrence of insulin resistance on target tissues of the body and the failure of pancreatic cells in the liver to produce more insulin (2). This deadlock can lead to obesity and Fatty liver.
Read: Treating Fatty Liver Naturally
6. High Fat Diet:
Eating a high-fat diet is one of the major causes of fatty liver disease. Along with fats, the high amounts of carbohydrates and proteins in the diet get converted to triglycerides. They are stored as fat cells and get accumulated on the liver, leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
7. Genetic Factors:
Genes play an important role in determining the risk of getting a fatty liver. According to research, patients with certain types of genes (PNPLA3) are more prone to getting Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis (3). One reason for this is that these genes may contain enzymes, which affect lipid metabolism and increase the accumulation of fat on the liver.
8. Medications And Steroids:
Long-term usage of certain medications like Steriods and Corticosteroids is known to cause drug-induced fatty liver. These drugs are known to injure the liver and disrupt its normal functionality. Some of these medicines can get converted to chemicals that can prove to be toxic to the liver and lead to Steatosis (Fatty Liver), Cirrhosis and even liver failure.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver:
Most people who are affected by Fatty Liver do not experience any major signs. However, as the grade progresses, one may experience some of these symptoms.
- Discomfort And Pain The Right Upper Quadrant: Inflammation of the liver can cause abdominal pain, typically on the right side of the body.
- Loss of Appetite: You might experience poor digestion and a feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen.
- Weight Loss: In complicated conditions like Liver Fibrosis or Cirrhosis, patients may experience gradual weight loss.
- Weakness and Fatigue: One may experience sluggishness and lack of energy due to fatty liver disease.
- Jaundice: You may notice yellowing of skin and eyes due to buildup of Bilirubin in blood.
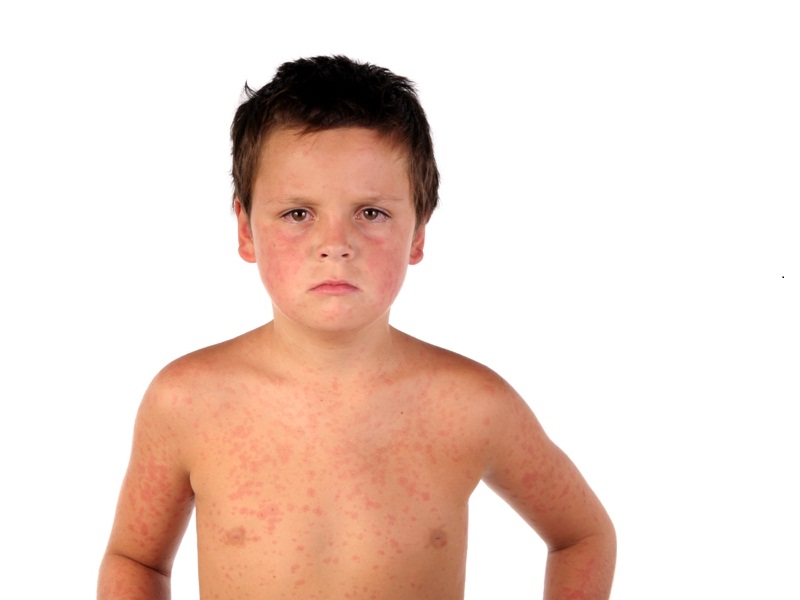
- Skin Rash: Symptoms like redness, skin rash and itching can occur in severe cases of fatty liver disease.
- Edema: Due to decreased protein production by the liver, patients may experience swelling of the abdomen and legs.
- Nausea: Some patients may experience nausea and vomitings due to the liver inability to eliminate the toxins from your body.
- Mental Confusion: The accumulated toxins in the liver can get deposited in the brain and cause mental confusion, lack of focus and gradually, unresponsiveness and coma.
Read: Obesity Treatment At Home
Risks and Dangers of Fatty Liver:
A simply Fatty Liver might not pose any immediate health risks to the body. However, when left untreated, the disease may progress to more serious conditions like Steatosis, Fibrosis and Cirrhosis. Here some of the dangerous complications of neglecting a Fatty Liver:
1. Liver Cancer:
It is known that continued alcohol consumption while having alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis may increase the risk of liver cancers and increase mortality.
2. Diabetes:
A study suggests that patients suffering from Fatty Liver are more prone to getting Type-2 Diabetes within 5 years of developing that condition(4). Irrespective of insulin resistance, those with fatty liver recorded higher glucose levels and lipid profiles than those who did not have fatty liver.
3. Coronary Artery Diseases:
Recent findings suggest that non-alcoholic fatty disease caused due to obesity can increase the risk of heart diseases like artery blocks. In extreme cases, it may even lead to heart attacks and failures.
That explains the symptoms and causes of fatty liver in detail! A basic understanding of these points can help you identify the problem early and take the right course of action. The best way to reverse or lower the severity of the condition is through lifestyle changes, which include a healthy diet and regular exercise. Speak to your doctor for more information on Fatty Liver disease!
Disclaimer: This article does not provide any medical advice and is intended for informational purposes only. It must not be treated as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers:
Q1. Is Fatty Liver Painful?
In most cases, fatty liver occurs without any noticeable symptoms. In advanced stages, patients may experience a dull pain in the right side of the abdomen. With time, it can progress into a stabbing pain that can be unbearable. You may also notice swelling in that area and pain that radiates into the back and right shoulder blade.
Q2. Can Low Vitamin D Cause Fatty Liver?
Yes! A recent study suggests that patients with low serum Vitamin D levels have higher chances of getting Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) (5). This vitamin is known to have anti-inflammatory effects on the liver and protect it from hepatic damage. It is also found that Vitamin D supplementation can improve the lipid profile levels, which can lower the severity of NAFLD.
3. Do Gallstones Lead To Fatty Liver?
Gallstones are formed when the cholesterol and bile get solidified into small crystals. These stones can get trapped in the opening of the bile duct and blocks the flow of bile from the liver. With time, the stones can cause liver scarring, cirrhosis and liver failure, in extreme cases.